North Western Dermatology provides a full range of services to treat all conditions of the skin, hair and nails. A consultation with a Dermatologist may give you access to medicines or therapies only available through a specialist.
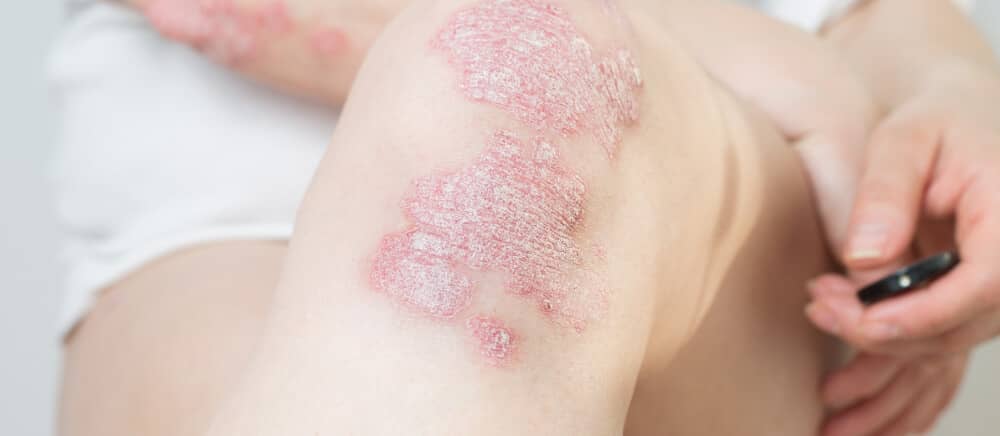
Psoriasis presents with thick scaly plaques on various parts of the body, including the scalp. Effective treatments are available, ranging from topical therapies and phototherapy to oral medications and newer “biologic” treatments.
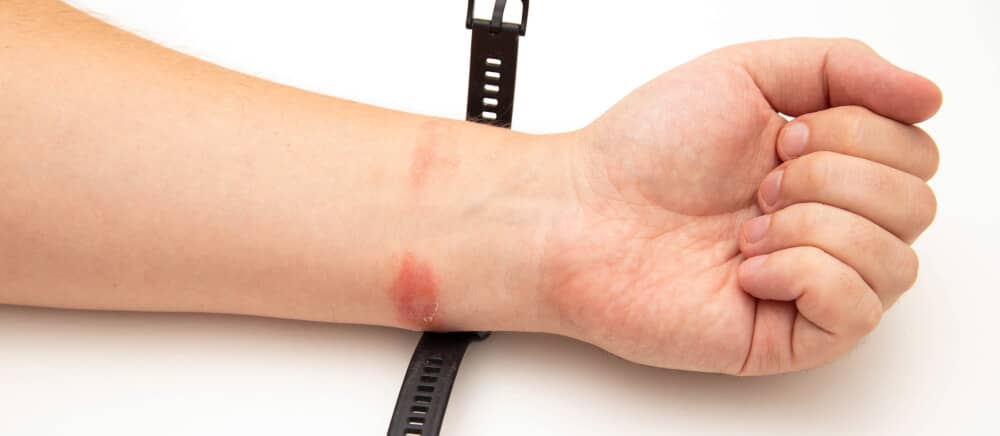
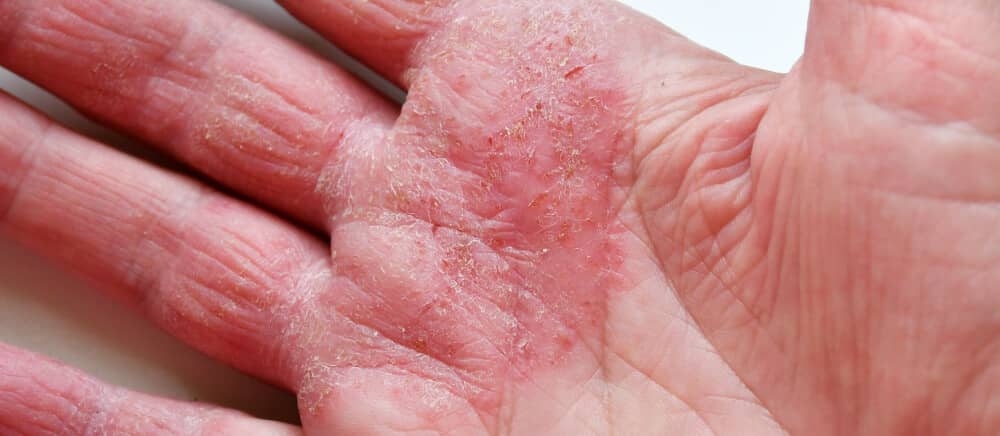

Some cases of eczema are due to chemical substances contacting the skin and causing an allergy. Allergens that cause this problem can be found in metal jewellery, cosmetics, fragrances, sunscreens and baby wipes.
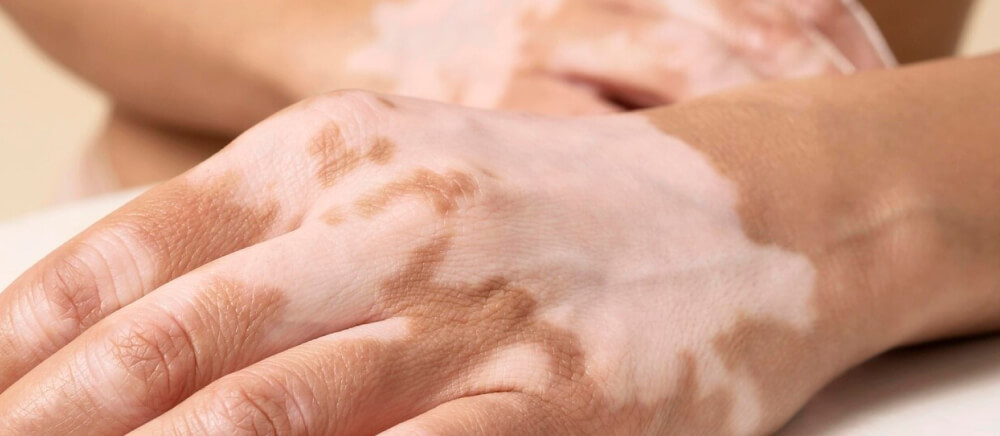

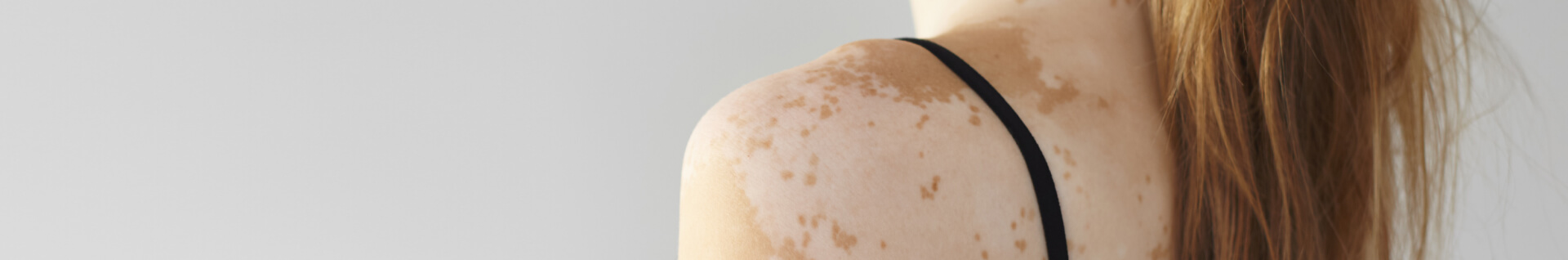
Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition that causes white patches to develop on the skin. Treatment, including phototherapy, is available but should be started early to prevent permanent pigment loss.
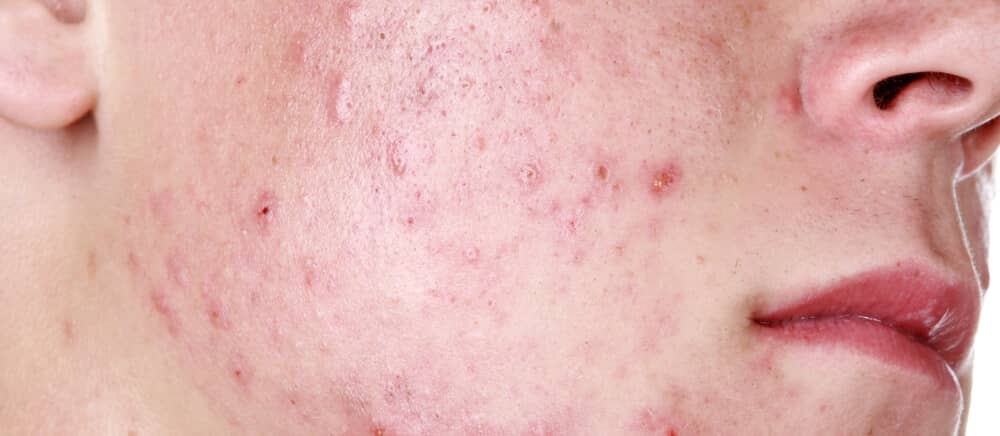
Acne is common and may result in psychological distress and sometimes permanent scarring. Dermatologist-only prescription medications provide the most effective treatment for severe cases.
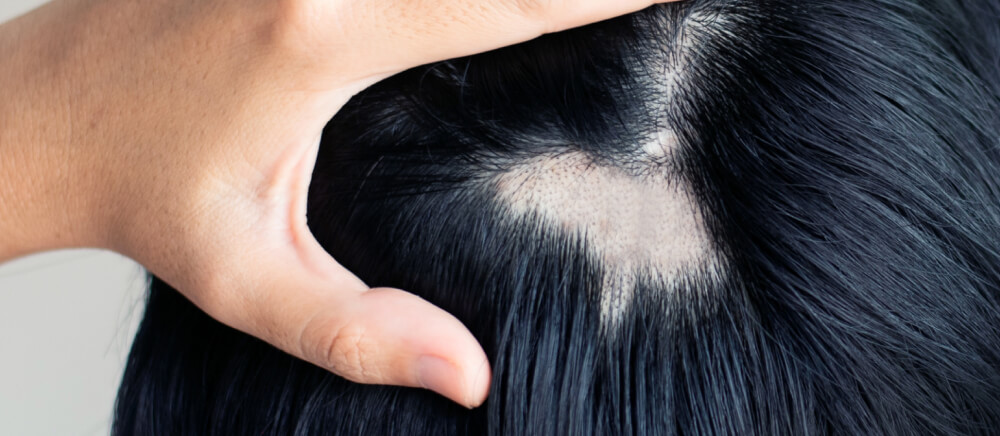


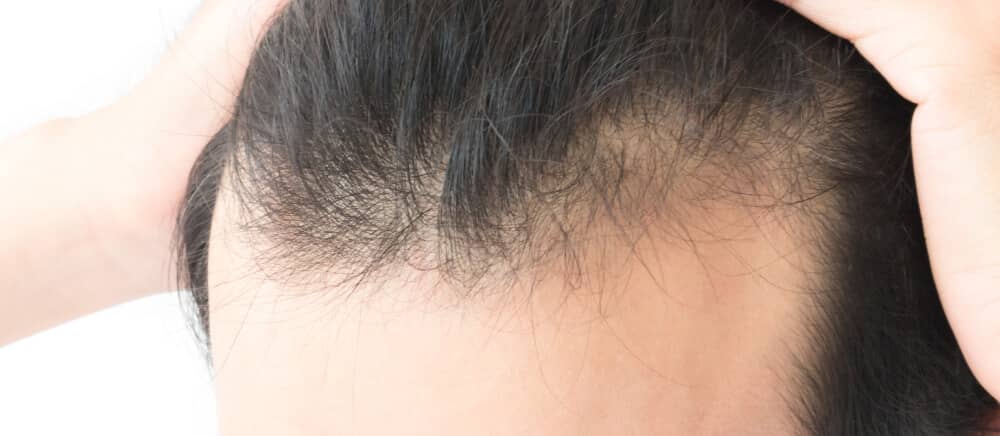
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as “male pattern baldness” or “female pattern hair loss”, is characterised by progressive hair thinning. Treatment can help slow hair loss and, and in many cases, promote hair re-thickening.

In dermatology, “topical” refers to any medication applied directly to the skin surface. Ointments are oil-based and greasy, making them ideal for dry skin conditions. Creams are lighter, easily absorbed, and suitable for general use, while lotions are more watery, making them well-suited for use on the scalp.
Topical steroids (also known as cortisones) play a key role in managing skin rashes. While generally safe, most are prescription medications that require supervision by a doctor, as overuse can lead to skin thinning. Dermatologists may also prescribe other topical treatments depending on the specific condition, and some of these may need to be specially prepared by a compounding pharmacist.
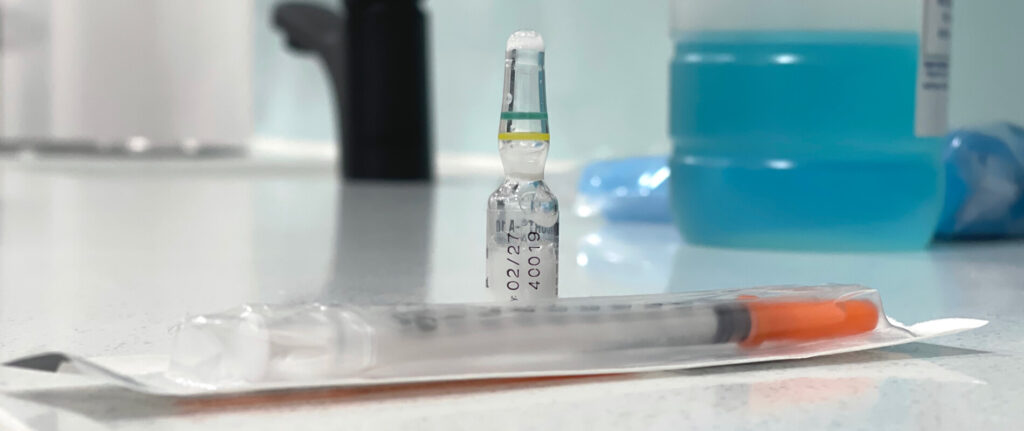
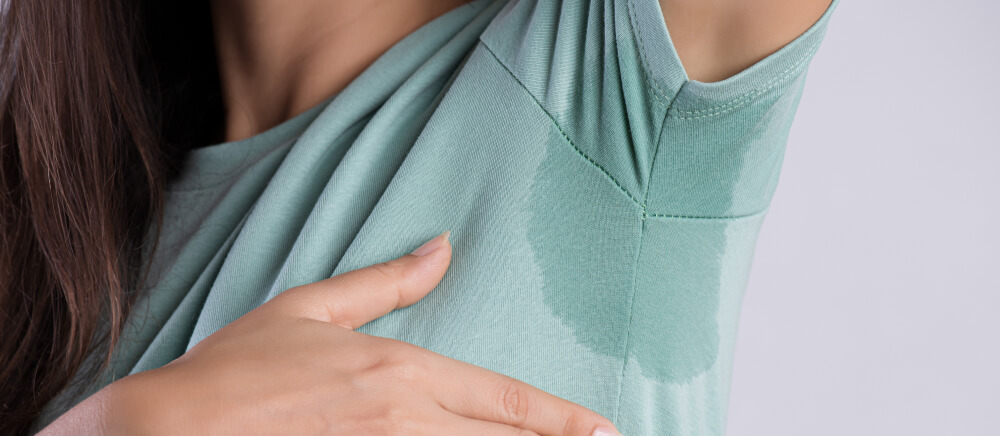
The term “intralesional injection” refers to the injection of medication directly into the affected area of the skin, known as the “lesion.” Dermatologists may recommend this approach when medication needs to be delivered deeper within the skin or targeted around hair follicles or sweat glands. Intralesional steroid injections are commonly used to treat conditions like alopecia areata and keloid scars. Other examples include the injection of bleomycin into warts and botulinum toxin into the underarm skin for managing hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating).

Phototherapy involves the use of artificial or natural sunlight to treat a range of skin conditions, including psoriasis, eczema, and vitiligo. Under a dermatologist’s supervision, narrowband UVB therapy provides a safe and effective treatment option, typically administered on-site two to three times a week. Each session lasts only a few minutes, and the cost is fully covered by Medicare. For conditions affecting only the hands and feet, a specialized machine targets these areas specifically.
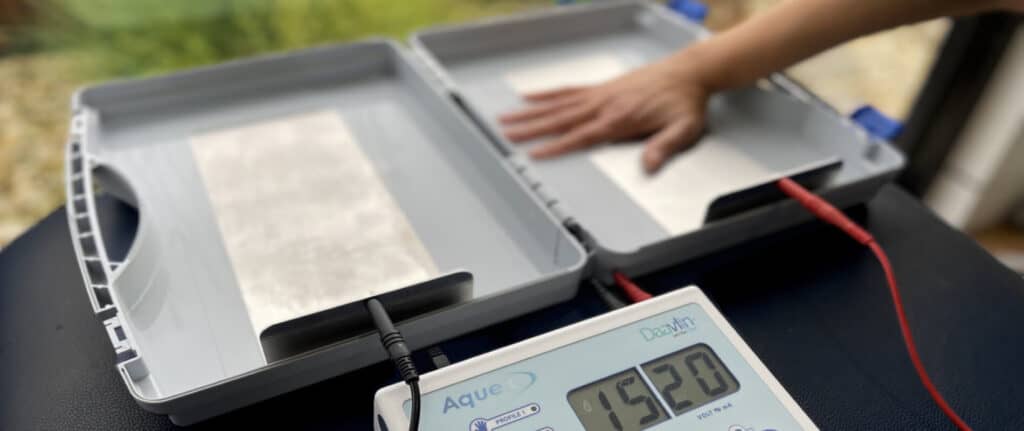

Iontophoresis is a safe and effective treatment for hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating) of the palms and soles. The device consists of two trays filled with a special salt solution. Once the hands or feet are placed in the solution, a low-voltage current is passed through, which directly reduces the activity of the sweat glands in the skin.
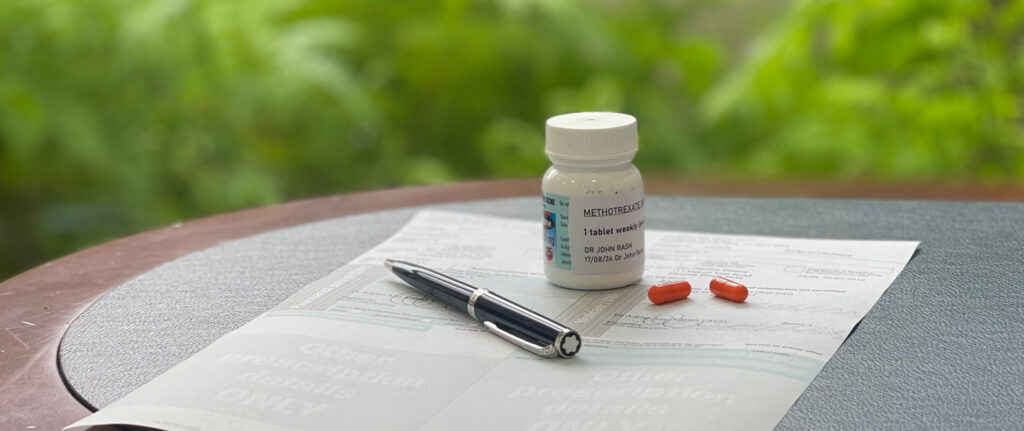
“Systemic therapy” refers to medications that enter the bloodstream, treating skin conditions from within the body. Dermatologists may prescribe oral medications for cases where topical therapy or phototherapy alone has not provided sufficient results.
Systemic therapy is generally used for skin, hair, or nail conditions that are widespread, have potential to cause scarring, or significantly affect a person’s quality of life. A newer class of systemic therapies, called biologics, are injected under the skin at regular intervals. These drugs, which target specific parts of the immune system, are highly effective but costly and can only be prescribed under the PBS by dermatologists in specific cases.
© 2006-2024 North Western Dermatology
Photography by Ayooluwatomiwa Oloruntoba